
Nowadays, various mature injection molding processes bring more creative space to designers and engineers. They can inspire their inspiration to enhance the appearance and ergonomics of the product.
Often a single material or color does not meet the manufacturing requirements of the product. The materials for these products range from plastics to metals.
In the past, this was done by using additional secondary services or more complex assemblies to create finished products. However, today’s multi-material injection molding largely eliminates these additional requirements, making it easier to manufacture complex finished products, faster, and cheaper.
What is multi-material injection molding?
It is a single component made from a combination of two or more plastic or elastomeric materials. You can read the definition in Wikipedia. Before that, I thought this was a category of overmolding.
I think overmolding is a big category. Only some parts are similar to multi-material injection molding or insert molding, so the overmolded part is classified into multi-material injection molding.
In fact, I also found different voices, but I prefer authority. Then I divide the multi-material injection molding into:
- Multi-component injection molding
- Multi-shot injection molding (MSM)
- Over-molding
Multi-shot injection molding (MSM)
Also referred to as sequential injection molding, multi-shot injection molding refers to creation of multiple layers relative to the starting axis of the initial mold. In other words, the warm, heated materials are inserted into the mold in a very specific sequence one after another.
This creates a layering effect between materials while maintaining relatively high-energy interactions at material boundaries. This is important because it implies that the inter-layer bonds are stronger in many cases than when the layers are applied to a previously cooled part, as is more closely the case of over molding. While there are other applications, this operation is preferred when varying molds (different geometries) are desired between material layers.
Multi-shot injection molding applications
This technology or process is nothing new, and is simply used for the production of two-color plastic parts or products. The two materials form a single plastic part by physical (snap, surface roll, thread) or chemical (co-bonding, miscible) bonding.
In some places, it is called 2k injection molding. 2K injection molding (MSM) is by far the most versatile, complex and interesting of the MMM process. It requires a specific two-color injection molding machine to complete the injection molding. Plastic parts need to be molded twice, but the product is only ejection once, usually by a set of molds.


3 types of mold structure
According to moving different mold parts can be divided into:
1. Rotary Platen Multi-Shot Molding
2.Index Plate Multi-Shot Molding
3.Core Toggle Multi-Shot Molding
Rotary Platen Multi-Shot Molding
Rotary Platen MSM is the simplest and most common category of MSM. The figure below shows a simplified schematic of a rotary platen MSM mold.
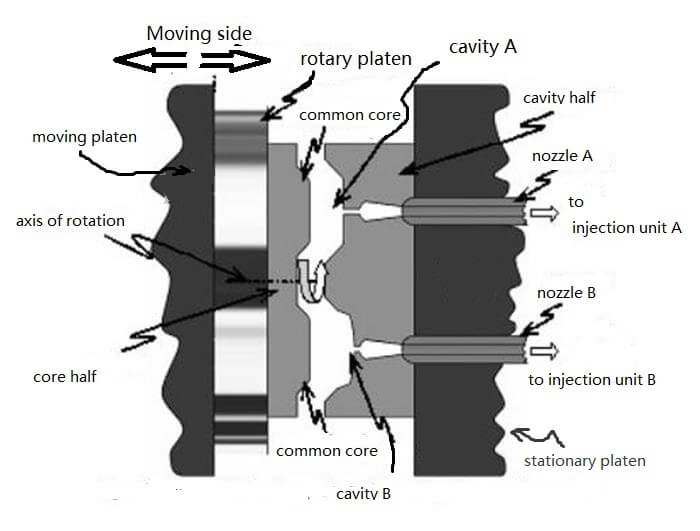
The mold feature is the rotating platen on the left side of the figure. The core plate contains two identical cores that are mirrored on the centerline of the platen and coincide with the axis of rotation. The cavity plate connected to the fixed platen contains two cavities with different geometries. Essentially, in each cycle, the rotating platen completes the switching of the injection molded parts. Eliminates the need for manual switching.
Molding process
The figure is a rotatable platen molding process is described as follows:
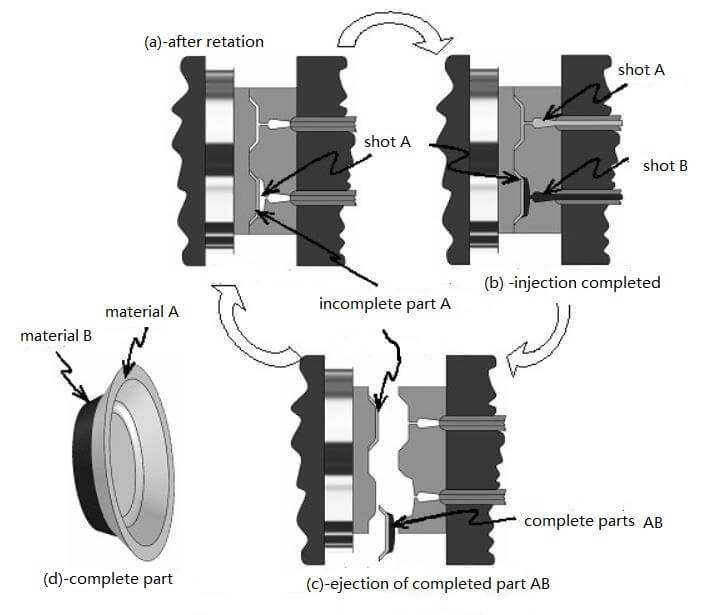
(1) Must first test whether the mold has reached a steady state. That is capable of producing a complete plastic parts. Make sure the mold can produce a complete plastic part.
(2) First, the plastic part A is completed in advance in the A cavity, and the plastic part A is a semi-finished product.The rotary table is rotated 180 degrees. Plastic part A enters the B cavity. As shown in Figure (a).
(3) The A and B cavities are simultaneously injection molded, but the finished plastic part A and the finished plastic part AB are produced.As shown in Figure (b).
(4) The mold is opened and the plastic part AB is ejected. The rotary table is rotated 180 degrees.Loop from (3) to (4).
pros and cons
Only two-material molds are shown here, which can actually accommodate more materials. Three- and four-cavity injection molding machines can also be used to make three materials and four materials.
The rotary platen can be rotated by 90°, 120° or 180° depending on the amount of material used.
The disadvantage is that a special molding machine is required to provide the required rotation on the core side. This can significantly increase the cost of the mold.
Index Plate Multi-Shot Molding
The indexing plate MSM is similar to the rotating platen MSM, adding additional capabilities: The rotating platen can now be retracted from the core half. In addition, the cavities and cores of each stage have different geometries. Indexing perform switching between different core / cavity sets. The figure below shows a simplified schematic of the indexing plate MSM mold.
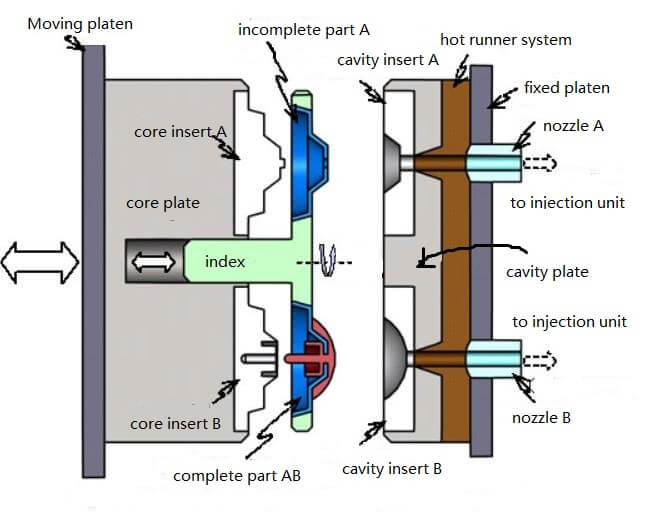
Injection molding process description
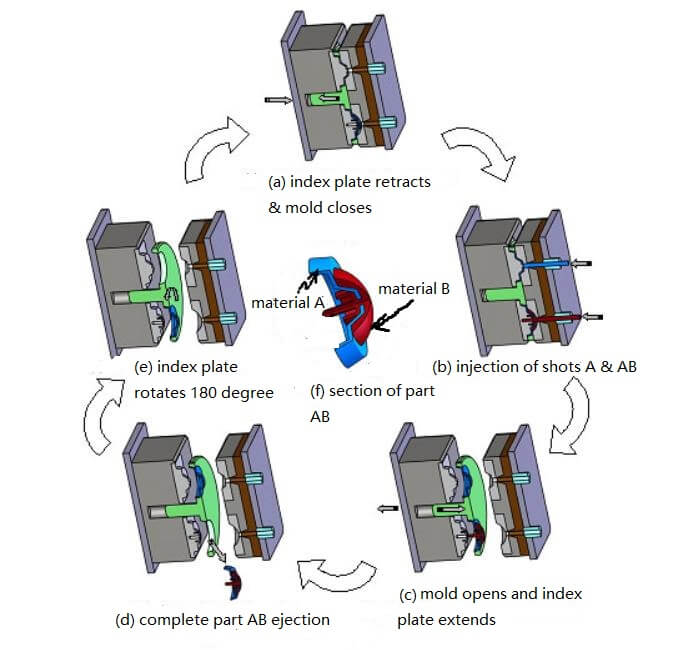
(1) Must first test whether the mold has reached a steady state. That is capable of producing a complete plastic parts. Make sure the mold can produce a complete plastic part. Close the mold and retract the indexing plate (as shown in (a) of the figure). The plastic part A is completed in advance in the A cavity, and the plastic part A is a semi-finished product. As the index plate returns, the plastic part A enters the B cavity.
(2) Materials A and B are simultaneously injected into their respective cavities and allowed to cool.This produces a complete component plastic part AB in cavity B, which produces a plastic part A in cavity A (as shown in (b) of the figure).
(3) The mold opens and the index board pops up(as shown in (c) of the figure).
(4) Then eject the complete component AB(as shown in (d) of the figure). A cross section of the complete assembly AB is shown in (f) of the figure.
(5) The indexing disc is rotated 180°, retracted onto the core and the mold is closed (as show in (e) of the figure).Repeated loop.
pros and cons
The indexing plate MSM is more complex than the rotating platen MSM and requires a more complex mold. This complexity further increases mold cost and time, but it allows for the production of more complex plastic parts.
Core Toggle Multi-Shot Molding
The core toggle MSM process is the easiest because the core and cavity of the mold do not need to be moved. Conversely, changing the geometry of the mold cavity by moving the slider.
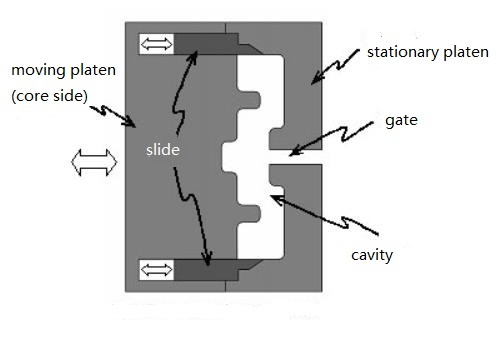
Process Description
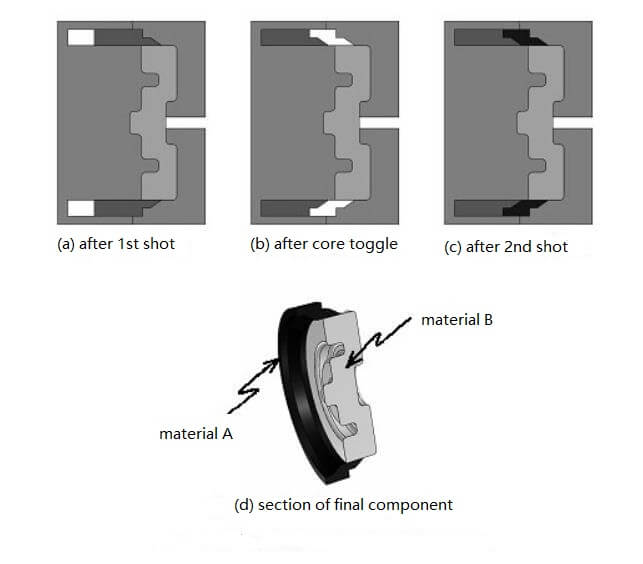
(1) inject material A into the cavity so that the slider is in the fully extended position (the far right in this example, Figure (a)).
(2) Retracting the slider to reveal a new portion of the cavity (left side in this example, Figure (b) ).
(3) Material B is injected into the reconfigured cavity through a separate gate (not shown), and the remaining gap is filled by moving the slider (Fig. (c)).
(4) The plastic part (Fig. (d))hardens and Ejected from the mold.
(5) Sequentially circulated from (1) to (4).
Pros and cons
Adding a slider to the mold adds cost to the tool, but it can still be much less expensive than rotating the platen or indexing plate mold. Unfortunately, it cannot produce complex plastic parts.
Overmolding Overview
Overmolding is a molded variant. This process is the addition of additional shapes and structural layers to existing components by injection molding of liquid resin. That the first material (sometimes referred to as the substrate) is partially or completely covered by the subsequent material (overmolding material) during the manufacturing process.
Among them, the substrate can be anything. For example: machining metal parts, molding plastic parts, and even existing products such as threaded inserts, screws or electrical connectors.
In a sense, overmolding includes insert molding and two-step injection molding.
Overmolding application
Overmolding can be a combination of any two materials. However, compatibility issues between the two materials must be considered.
Typical application:
Plastic plastic: a combination of plastics of different materials and colors. In fact, it’s a bit like 2k injection molding.
Plastic-rubber: a combination of rigid plastic and soft rubber/TPE. It is usually provided with a soft grip surface for rigid plastic parts. Metals and rubber can do the same.
Metal-Plastic: Reduces subsequent processing with one-step molding. Eliminate assembly time.

2 step molding
A part of a material is formed on an injection molding machine, then the part is placed as an insert in another mold. And a second material is injected.
In fact, 2 step molding and 2k injection molding are similar. The difference is that 2 step molding does not require a specific injection molding machine. This can be done using standard injection molding. But two different sets of molds are needed.
Compared with 2k injection molding, the plastic parts have a high defect rate and the mold cost is high. However, 2 step molding uses a high degree of flexibility. A substrate mold can be combined with a variety of cladding materials to achieve different types of products.
Insert molding
Insert molding is the insertion of an insert into an injection mold and injection molding of the part. The insert is usually a metal part. Insert molding can enhance the mechanical properties of plastic parts. This avoids secondary installation and reduces costs.
Insert molding application
A typical application for insert molding is to include one or more threaded metal inserts in a plastic part. For example, threads in plastic parts may wear out during repeated use, which may result in component failure. Metal inserts help to enhance the performance of the plastic and ensure reliable fastening when reusing parts.
This combination of plastic and metal allows the designer to take advantage of the weight of the plastic and the strength of the metal. Insert molding can also be used as a package for electronic components to enhance the performance of electronic components. You can click here to learn more about LPM.

Multi-component injection molding
Also known as co-injection molding. Also known as co-injection molding. Multi-component injection molding describes the simultaneous injection of multiple viscous materials. Instead of using one material as an additional layer relative to another material.
In other words, it creates a sandwich structure. That is, one material completely coats another material as shown in the figure:
Co-injection application
This advanced molding technology has been around for decades. Early success in professional applications such as ketchup containers, stadium beer bottles and medical vials. With the upgrade of manufacturing services, it can perform better.
Pros and cons
- Reduce costs by using cheaper filler materials as the invisible core of the product
- Change the density and elasticity of the product so that it floats in water or absorbs shock.
Despite these advantages, co-injection requires machines that are more expensive and difficult to maintain than standard single injection machines. The co-injection process also has difficulty handling complex geometries.
The end of the article
Multi-material injection molding gives the product more molding options. If you want to improve the appearance of the plastic part, let it be layered, you can consider Multi-shot injection molding. You want to make your product lighter, do you consider co-injection molding? You want plastic parts to have better mechanical properties, consider insert molding. Enjoy your creativity. You didn’t find a better solution? Maybe you can hand it over to us. contact us.
